Picture this: a giant cargo ship slicing through blue waters, carrying thousands of tons of goods. From the deck, everything looks smooth and efficient. But below the surface, the ship’s hull is often covered with algae, barnacles, and mussels. This layer, known as biofouling, increases drag and forces the vessel to burn more fuel. The solution is hull cleaning.
On the surface, cleaning seems straightforward. You scrub away unwanted organisms, restore efficiency, and sail faster. But like many things at sea, it’s not that simple. Hull cleaning has environmental impacts that ripple across ecosystems. From toxic paint particles polluting waters to invasive species hitching rides into new habitats, these impacts can be both immediate and long-term.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into why hull cleaning matters, the risks it poses, the regulations shaping practices, the costs involved, the eco-friendly solutions emerging, and what the future holds. By the end, you’ll know not just the challenges but also the opportunities to clean smarter and greener.
Why Hull Cleaning Matters
Ships are the backbone of international trade, carrying over 80% of global commerce, according to the International Maritime Organization (IMO). Yet, fouled hulls make them less efficient and more polluting.
- Fuel Efficiency
A fouled hull can increase resistance by up to 40%. More drag means more engine power required, leading to higher fuel consumption. This directly ties into operational costs. - Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Burning extra fuel doesn’t just hurt profits—it increases emissions of carbon dioxide, sulfur oxides, and nitrogen oxides, worsening climate change. - Compliance
International conventions, such as MARPOL (explained by Marine Insight), require ships to minimize pollution. Hull condition is a silent compliance factor. - Operational Performance
A clean hull ensures smooth voyages, predictable schedules, and less wear on engines.
Simply put, hull cleaning isn’t just about looks—it’s about sustainability, profitability, and compliance. Yet, it brings its own environmental impacts that operators must manage responsibly.
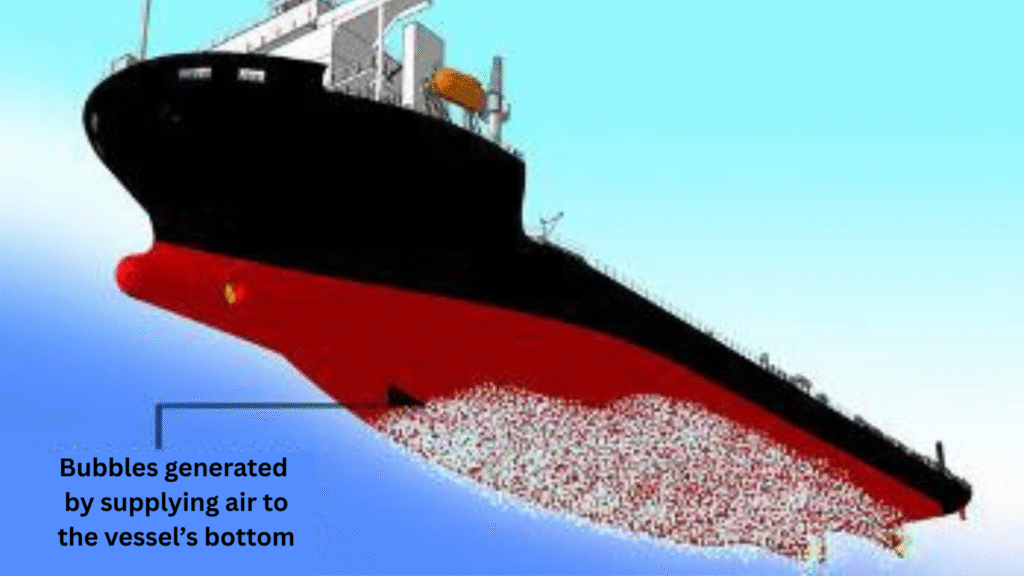
Environmental Impacts of Hull Cleaning
Pollution Risks
When cleaning scrapes away marine organisms, it often removes antifouling paints too. These paints contain copper and biocides—substances toxic to marine life. If uncontrolled, they dissolve into surrounding waters, harming fish, corals, and plankton.
Think of it like peeling off old house paint. Instead of falling on the ground, these chips sink into ecosystems where fragile marine species live.
✅ 4 Things to Check for Safety at Sea pic.twitter.com/dAxhJQ2i6U
— Marine Super Cargo (@Marinsupercargo) September 14, 2025
Invasive Species Spread
One of the most concerning environmental impacts is biological contamination. Fouling organisms dislodged during cleaning can drift into new waters, establishing invasive populations.
A real-world example: The Mediterranean saw rapid growth of non-native mussels that originally came attached to ship hulls. Such invasions can outcompete local species, disrupt fishing industries, and cost millions in ecological restoration. (IAPH)
Paint and Coating Damage
Overly aggressive methods, such as abrasive brushes or divers scraping manually, can strip protective coatings. This not only increases corrosion risk but also adds more toxic particles to the sea. The unintended result? Greater environmental impacts and higher maintenance costs.
Waste Disposal Challenges
Hull cleaning generates sludge-like debris—a mix of biofouling, paint flakes, and chemicals. If containment systems aren’t used, this debris floats freely, clouding waters and reducing sunlight penetration. Seagrasses, corals, and plankton suffer as photosynthesis becomes harder. Learn more
These four risks highlight why hull cleaning, if unmanaged, can do as much harm as good.
Regulations and Compliance
To counter these environmental impacts, global frameworks set clear rules.
- IMO Guidelines
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) provides global standards for safe in-water cleaning. - MARPOL Convention
As detailed by Marine Insight, MARPOL regulates discharges from ships, including wastes generated during hull cleaning. - IMCA Standards
The International Marine Contractors Association (IMCA) offers operational best practices, ensuring safe and environmentally sound procedures. - Port Authority Rules
Many ports ban in-water cleaning unless advanced containment is used. For instance, Scandinavian ports enforce strict monitoring to avoid releasing invasive species. - IAPH Initiatives
The International Association of Ports and Harbors (IAPH) supports harmonized cleaning practices worldwide.
Compliance isn’t just about avoiding fines—it’s about demonstrating responsibility toward oceans that sustain global trade.
Cost Implications
Ignoring hull cleaning or doing it poorly carries significant financial consequences.
- Fines and Penalties
Non-compliance with MARPOL or local port rules can lead to fines in the hundreds of thousands. - Fuel Costs
A fouled hull can increase fuel consumption by up to 20%, burning profits alongside oil. - Maintenance Costs
Premature coating damage means costly dry-docking and repainting. - Case Study
A tanker operating in Asia faced fines after abrasive cleaning released pollutants. Switching to eco-robotic methods reduced violations and saved 15% on fuel annually.
These numbers show how managing environmental impacts effectively leads to both cost savings and operational stability.
Eco-Friendly Solutions
The maritime industry is innovating rapidly to reduce the negative environmental impacts of hull cleaning.
Robotic Hull Cleaning
Autonomous robots equipped with cameras and soft brushes clean precisely without damaging coatings. Many include debris-capturing systems, preventing waste discharge.
Containment and Filtration Systems
Advanced vacuums and filters capture biofouling and paint debris, ensuring no pollutants escape into open waters.
Nanotechnology and Biocide-Free Coatings
New coatings repel fouling organisms without toxic chemicals. These self-polishing surfaces reduce cleaning frequency, extending intervals between dry-dockings.
Cavitation Jet Cleaning
Instead of abrasives, high-pressure water jets with microbubbles remove fouling gently, preserving paint integrity.
Service Providers Leading Change
Companies like CleanShip.co are pioneering sustainable solutions by combining robotics with compliance-driven cleaning protocols. Their practices reduce fuel use, protect coatings, and safeguard marine ecosystems.
These innovations prove that efficiency and environmental responsibility can go hand in hand.
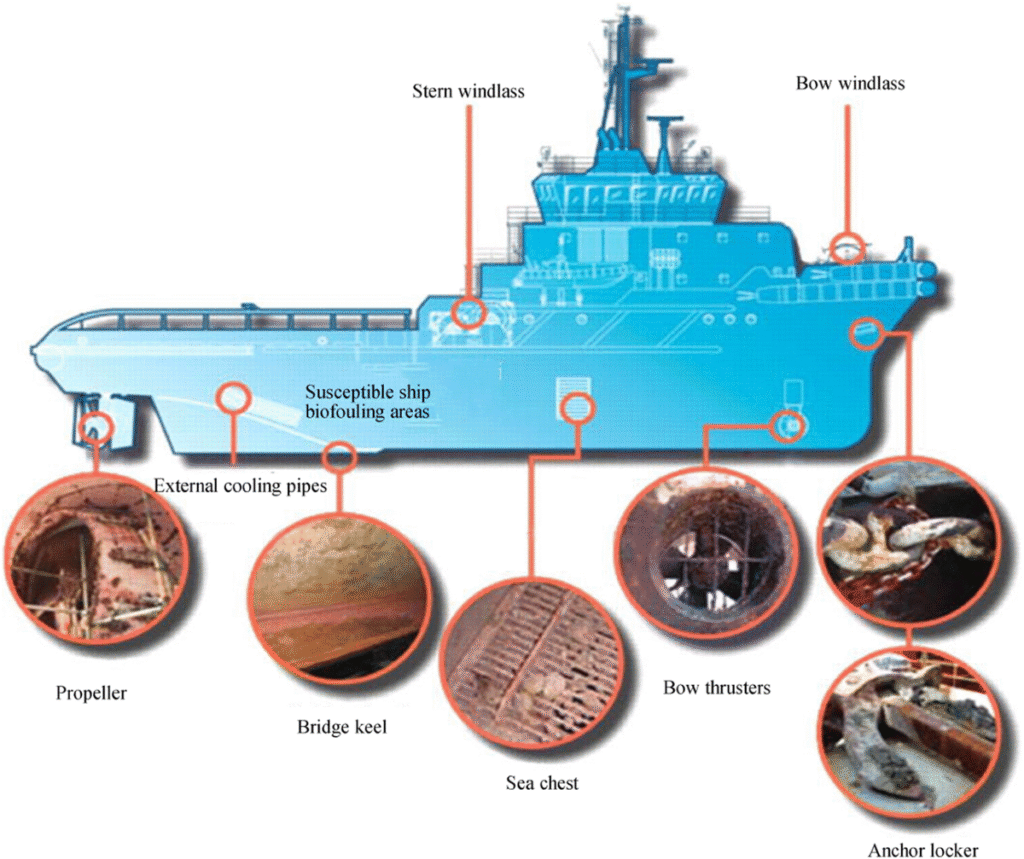
Future Trends in Hull Cleaning
The next decade will see hull cleaning evolve from a reactive task into a proactive, data-driven discipline.
- AI-Driven Cleaning Schedules
Artificial intelligence will predict fouling buildup using sensors and link cleaning frequency with real-time fuel consumption data. - Global Standardization
As IAPH and IMO push for harmonized policies, expect unified eco-cleaning standards worldwide. - Next-Generation Coatings
Nanotech and silicone-based coatings will dominate, reducing dependency on toxic antifouling paints. - Sustainability Certification Pressure
Shipowners will increasingly face demands for environmental certifications from charterers and regulators, making eco-cleaning a business advantage.
Future practices will minimize environmental impacts not just by cleaning smarter, but by preventing fouling in the first place.
Conclusion
Hull cleaning is more than a maintenance activity—it’s a critical factor in global shipping efficiency, compliance, and environmental stewardship. The environmental impacts range from pollution and invasive species to coating damage and waste disposal. But by adopting modern solutions, following regulations, and choosing eco-responsible providers, ship operators can turn challenges into opportunities.
The path forward is clear: stay compliant, embrace innovation, and protect our oceans. Partnering with experts like CleanShip.co ensures that hull cleaning not only boosts performance but also safeguards marine ecosystems for future generations.
FAQs:
Q1. Why does hull cleaning cause environmental impacts?
Because the process can release toxic paint particles, chemicals, and biofouling waste into the ocean, harming marine life if not contained.
Q2. How do invasive species spread through hull cleaning?
Organisms detached during cleaning can survive in new waters, establishing invasive colonies that disrupt ecosystems and fisheries.
Q3. What regulations govern hull cleaning practices?
Key rules come from the IMO, MARPOL (via Marine Insight), IMCA, and local port authorities.
Q4. Are robotic hull cleaners more eco-friendly?
Yes. Robots use precise cleaning methods and containment systems, reducing coating damage and preventing waste discharge into the sea.
Q5. How can ship operators reduce environmental impacts while saving costs?
By adopting eco-friendly coatings, scheduling regular cleanings, following compliance standards, and partnering with providers like CleanShip.co.


