When you look at a massive cargo ship gliding over the ocean, it appears that sheer engine power drives its journey. But hidden beneath the waves, an often-overlooked factor determines how much fuel that vessel consumes: the state of its hull. In fact, the correlation between fuel efficiency and hull condition is one of the strongest influences on operating costs, emissions, and compliance today.
Imagine a world-class swimmer. With a streamlined body, they glide efficiently through the water. But if that same swimmer wore a weighted, rough-textured suit, every stroke would take more effort and burn more energy. Ships face the same fate when their hulls are fouled, corroded, or neglected.
In this long-form guide, we’ll explore the science, economics, compliance, and future innovations surrounding fuel efficiency and hull condition, giving you the context you need as a ship operator, manager, or owner to make smarter decisions.
Understanding the Connection Between Fuel Efficiency and Hull Condition
At its core, fuel efficiency in shipping is about extracting maximum performance while using the least fuel. Hull condition means the physical state of the vessel’s submerged surface—clean or fouled, smooth or rough, strong or corroded.
- A clean, smooth hull = low resistance, better speed, lower fuel burn.
- A fouled or rough hull = high resistance, reduced speed, higher fuel burn.
This balance illustrates why fuel efficiency and hull condition are inseparable. Hydrodynamic principles, which govern how water flows over surfaces, amplify small imperfections into huge performance losses.
The Science of Drag and Resistance
When a hull interacts with seawater, two main types of resistance come into play:
- Frictional Resistance: Caused by water clinging to the roughness of the hull’s outer layer. Even a biofilm just 0.1 millimeters thick increases this resistance.
- Form and Wave Resistance: Turbulent flows and wake patterns generated by hull irregularities add further drag.
Real-world studies show:
- A lightly fouled hull may cause a 10–20% fuel penalty.
- Heavy fouling (barnacles, mussels) may spike fuel consumption by 30–40%.
- Across global fleets, poor hull conditions waste $6–8 billion annually on extra bunker fuel.
That’s why focusing on fuel efficiency and hull condition isn’t optional. It directly impacts competitiveness.
What Fouling Does to Fuel Efficiency
Biofouling includes:
- Microfouling: Slime and microorganism films.
- Macrofouling: Barnacles, mussels, algae, seaweed.
Once established, these layers thicken the boundary layer between water and the hull. The result is like dragging an anchor through the water:
- Increased engine load: Engines must burn more fuel for the same speed.
- Speed loss: Vessels can lose up to 2 knots.
- Unplanned dry-docking: Heavy fouling shortens maintenance cycles dramatically.
The invisible link between fuel efficiency and hull condition becomes painfully visible when fuel bills spike and voyage schedules slip off track.
Learn more about: Underwater hull cleaning.
Why This Matters to Owners and Operators
Think of fuel efficiency and hull condition correlation as a three-way impact:
- Economic Pressure
- Fuel accounts for 40–60% of operating costs in shipping.
- Cleaning and hull coating costs are negligible compared to wasted bunkers if ignored.
- Compliance and Regulation
- IMO’s Carbon Intensity Indicator (CII) and MARPOL Annex VI penalize inefficiency.
- Fouled hulls mean poor CII ratings, lower charter rates, and possible regulatory sanctions.
- Environmental Responsibility
- Higher emissions equal reputational risks.
- Fouling also spreads invasive marine species, a growing concern under IMO biofouling guidelines.
For modern operators, aligning fuel efficiency and hull condition helps safeguard profits, compliance, and environmental commitments simultaneously.
Case Studies Demonstrating the Link
Real-world evidence confirms that fuel efficiency and hull condition are inseparably linked. Across naval fleets, commercial shipping, and international organizations, studies consistently show that fouling isn’t just a maintenance issue—it’s an operational cost driver.
1. U.S. Navy Research
The U.S. Navy has long invested in studying the relationship between fouling and fuel efficiency. Their findings reveal that regular underwater hull cleanings deliver fuel savings of up to 15% per vessel. Given that naval operations run on tight budgets and mission-critical schedules, these savings directly translate into extended range, reduced refueling needs, and lower greenhouse gas emissions. For a large fleet, even a single percentage gain compounds into millions saved annually.
2. Commercial Tankers
For commercial tanker operators, time is money. Studies documented that neglecting hull cleaning for just six months led to an average speed loss of over 1 knot. At first glance, this may not seem dramatic, but over a transoceanic voyage, it forces operators to burn significantly more fuel to maintain chartered schedules. The result? Higher voyage costs, lost competitiveness in the charter market, and increased regulatory scrutiny due to higher CO₂ emissions per nautical mile.
3. IMO Reports
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has repeatedly emphasized the economic and environmental toll of fouling. Their reports highlight that biofouling accounts for one of the most underestimated fuel penalties in the global shipping industry. IMO estimates suggest billions of dollars in annual losses due to increased drag and associated fuel consumption. Moreover, the issue compounds environmental risks—every extra ton of fuel burned means higher CO₂, NOₓ, and SOₓ emissions, threatening compliance with MARPOL Annex VI and the IMO’s GHG reduction strategy.
IMO meets this week to discuss implementation of IMO instruments:
— International Maritime Organization (@IMOHQ) July 22, 2024
✅ analysis of marine casualties, including lessons learned
✅ fishing safety & Cape Town Agreement
✅ Port State control issues
✅ guidance on remote surveys
Remarks by @IMOSecGen here: https://t.co/fYFlbd0EKm pic.twitter.com/PgpNkaySou
Practical Steps to Enhance Fuel Efficiency by Managing Hull Condition
So, how do you, as a ship owner or manager, tackle this challenge?
- Scheduled Underwater Inspections
Trained divers or remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) can detect fouling before it becomes a crisis. - Proactive Hull Cleaning
Instead of waiting for fouling to degrade performance, scheduled scrubbing or polishing retains maximum smoothness. - Antifouling and Foul-Release Coatings
Advanced coatings (like silicone-based or biomimetic sharkskin-inspired paints) reduce the adhesion of organisms to hull surfaces. - Data-Driven Performance Monitoring
Software tools track speed and fuel fluctuations, giving early signals when a hull starts losing efficiency. - Follow Guidelines
Align practices with IMO, IMCA, and IAPH rules to ensure cleanings are environmentally safe.
By embedding these steps into operations, the correlation between fuel efficiency and hull condition becomes a managed variable, not an unpredictable threat.
Compliance, Regulations, and Market Pressure
Ship efficiency is no longer voluntary—it’s regulated and monetized.
- IMO CII Ratings: Measure efficiency over time; poor hull condition means worse ratings.
- EEXI (Energy Efficiency Existing Ship Index): Demands vessels meet minimum performance standards.
- IAPH Guidelines: Ports increasingly restrict in-water cleaning unless waste capture systems are used.
Failing to respect the link between fuel efficiency and hull condition not only costs fuel money, but it can also cost your fleet operating licenses and charter contracts.
Environmental Concerns
A neglected hull isn’t just a fuel problem—it’s an ecological issue:
- Fouling organisms detach in new ecosystems, spreading invasive species.
- Poor hull care raises emissions, worsening climate impact.
- Authorities are tightening port laws to curb biofouling-related environmental damage.
Therefore, maintaining hulls clean doesn’t only boost fuel efficiency and hull condition alignment—it safeguards oceans.
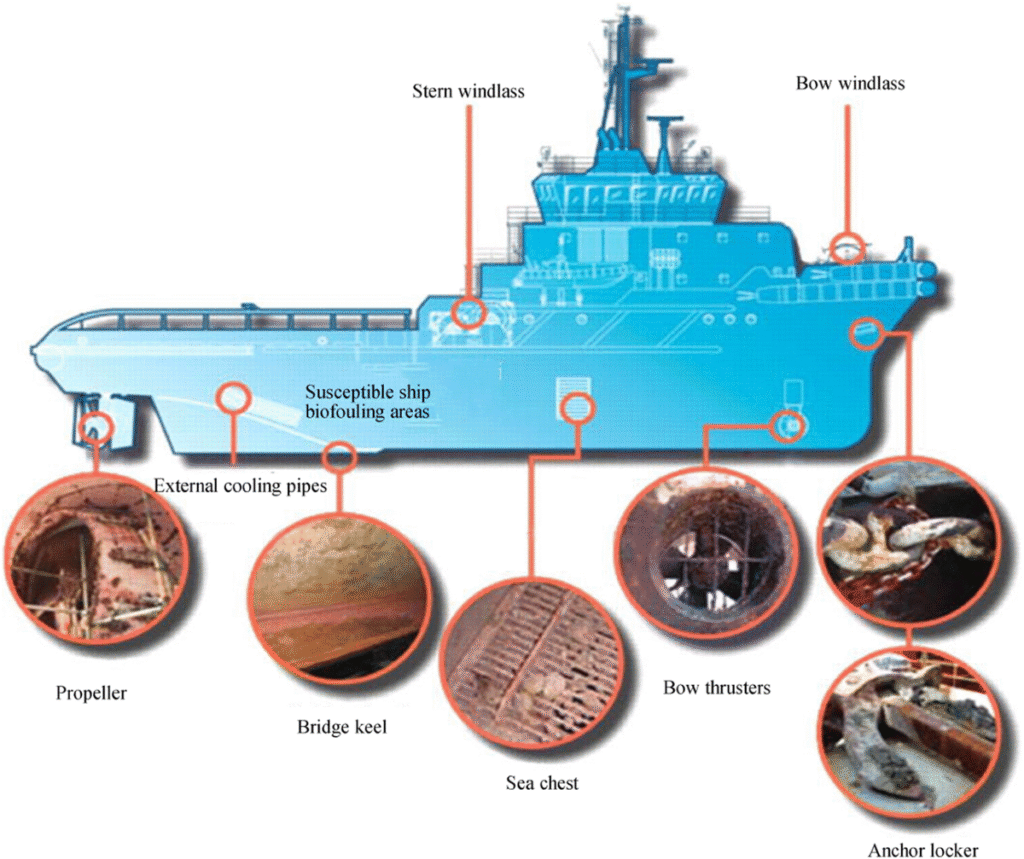
Future Innovations and Trends
The shipping industry’s fight against inefficiency and fouling is evolving with technology:
- Automated Robotic Cleaners: In-water robots clean while ships are docked, preventing fouling buildup altogether.
- Smart Hull Monitoring Sensors: Continuous real-time tracking of fouling through AI-based data collection.
- Biomimetic Textures: Inspired by shark skin and dolphin epidermis, coatings reduce drag naturally.
- Non-toxic Nanocoatings: Future paints will use molecular repellents to prevent settlement, avoiding toxic leaching.
The future of maintaining fuel efficiency and hull condition lies in smarter, greener, and more predictive strategies.
Conclusion
The correlation between fuel efficiency and hull condition is undeniable. From hydrodynamic drag to rising fuel bills, IMO compliance, and environmental protection—hull care impacts it all. To recap:
- Fouling increases drag, burns more fuel, and causes costly inefficiencies.
- Clean hulls safeguard compliance with IMO, MARPOL, and port authority regulations.
- Long-term fleet competitiveness demands proactive monitoring, cleaning, and new innovations.
Treat your hull as the ship’s skin—protect it, and you’ll protect both profitability and sustainability. For practical, eco-safe strategies, consider expert resources like CleanShip.co.
FAQs
Q1. Why do fuel efficiency and hull condition matter together?
Because hull roughness directly impacts how water flows around the vessel, influencing drag and fuel burn. Smoother hulls mean better efficiency.
2. What percentage of fuel loss comes from fouling?
Depending on severity, fouling can push extra consumption by 20–40%, wasting millions of dollars per year for commercial shipping operators.
3. How often should ships undergo hull cleaning?
Intervals vary by route and water conditions, but regular inspections every 3–6 months can prevent severe fouling from escalating.
4. Are antifouling coatings harmful to the environment?
Traditional ones used toxic biocides, but new coatings use silicone release layers or biomimetic technologies to reduce impact safely.
5. What’s the future of managing hull condition?
Expect AI-based performance tracking, autonomous robotic hull cleaners, and green coatings, all designed to maximize fuel efficiency and hull condition alignment.


